알고리즘/BAEKJOON
[백준] 2239 스도쿠 (Java)
kyeee2
2022. 4. 6. 15:04
[2239 스도쿠]
난이도: 골드4
2239번: 스도쿠
스도쿠는 매우 간단한 숫자 퍼즐이다. 9×9 크기의 보드가 있을 때, 각 행과 각 열, 그리고 9개의 3×3 크기의 보드에 1부터 9까지의 숫자가 중복 없이 나타나도록 보드를 채우면 된다. 예를 들어 다
www.acmicpc.net

문제
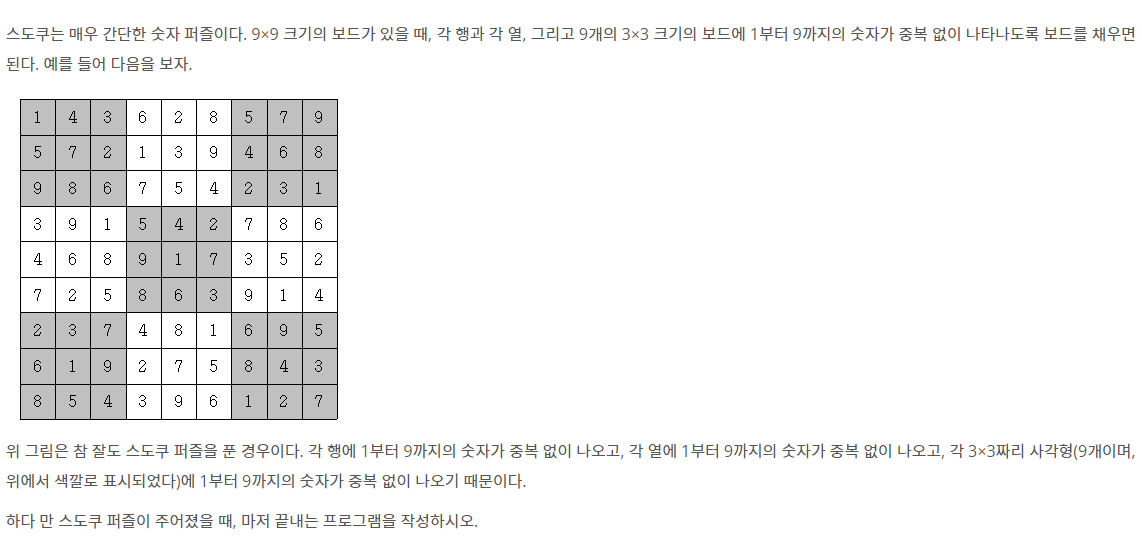
입력

출력

[아이디어]
백트래킹을 사용하여 가지치기를 하였다.
처음에는 빈칸에 하나의 수를 결정할 때마다 for문을 통하여 가능한지의 여부를 찾았다. 시간초과가 뜨지 않았지만 다른 사람들이 시간을 훨씬 덜 쓰길래 찾아보았더니 for문을 사용하여 가능하지를 따지지 않고 따로 배열을 생성하여 체크하는 방법을 알게되었다.
i행에 쓰인 숫자를 체크하는 배열 -> row[][]
i열에 쓰인 숫자를 체크하는 배열 -> col[][]
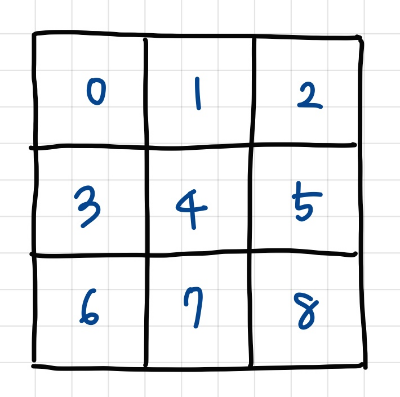
위의 그림처럼 사각형 안에 쓰인 숫자를 체크하는 배열 -> square[][]
이 때 몇 번째 square에 들어가는지는 (행 / 3) * 3 + (열 / 3) 으로 계산해주었다.
[JAVA 코드]
따로 배열을 만들어서 푼 방법
// 메모리: 17316KB
// 실행시간: 424ms
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder();
static int N = 9;
static boolean flag = true;
static int [][] sudoku = new int [N][N];
static boolean [][] row = new boolean [N][10];
static boolean [][] col = new boolean [N][10];
static boolean [][] square = new boolean [N][10];
static List<Point> zeros = new ArrayList<>();
static class Point {
int r, c;
public Point(int r, int c) {
this.r = r;
this.c = c;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
for(int r = 0; r < N; r++) {
String line = br.readLine();
for(int c = 0; c < N; c++) {
sudoku[r][c] = line.charAt(c) - '0';
if(sudoku[r][c] == 0) zeros.add(new Point(r, c));
else {
row[r][sudoku[r][c]] = true;
col[c][sudoku[r][c]] = true;
square[(r / 3) * 3 + (c / 3)][sudoku[r][c]] = true;
}
}
}
dfs(0);
System.out.println(output);
}
private static void dfs(int idx) {
if(!flag) return;
if(idx == zeros.size()) {
for(int r = 0; r < N; r++) {
for(int c = 0; c < N; c++) {
output.append(sudoku[r][c]);
}
output.append("\n");
}
flag = false;
return;
}
int r = zeros.get(idx).r;
int c = zeros.get(idx).c;
for(int n = 1; n < 10; n++) {
if(!row[r][n] && !col[c][n] && !square[(r / 3) * 3 + (c / 3)][n]) {
sudoku[r][c] = n;
row[r][n] = true;
col[c][n] = true;
square[(r / 3) * 3 + (c / 3)][n] = true;
dfs(idx + 1);
sudoku[r][c] = 0;
row[r][n] = false;
col[c][n] = false;
square[(r / 3) * 3 + (c / 3)][n] = false;
}
}
}
}
처음에 따로 배열을 만들지 않고 푼 방법
더보기
// 메모리: 21308KB
// 실행시간: 852ms
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Solution {
static BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
static StringBuilder output = new StringBuilder();
static int N = 9;
static boolean flag = true;
static int [][] sudoku = new int [N][N];
static List<Point> zeros = new ArrayList<>();
static class Point {
int r, c;
public Point(int r, int c) {
this.r = r;
this.c = c;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
for(int r = 0; r < N; r++) {
String line = br.readLine();
for(int c = 0; c < N; c++) {
sudoku[r][c] = line.charAt(c) - '0';
if(sudoku[r][c] == 0) zeros.add(new Point(r, c));
}
}
dfs(0);
System.out.println(output);
}
private static void dfs(int idx) {
if(!flag) return;
if(idx == zeros.size()) {
for(int r = 0; r < N; r++) {
for(int c = 0; c < N; c++) {
output.append(sudoku[r][c]);
}
output.append("\n");
}
flag = false;
return;
}
int r = zeros.get(idx).r;
int c = zeros.get(idx).c;
for(int n = 1; n < 10; n++) {
sudoku[r][c] = n;
if(isPossible(r, c)) {
dfs(idx + 1);
}
sudoku[r][c] = 0;
}
}
// 이 부분이 시간을 많이 잡아먹는다
private static boolean isPossible(int r, int c) {
// 사각형
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
if(r - r % 3 + i == r && c - c % 3 + j == c) continue;
if(sudoku[r - r % 3 + i][c - c % 3 + j] == sudoku[r][c]) return false;
}
}
// 가로
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if(c == i) continue;
if(sudoku[r][i] == sudoku[r][c]) return false;
}
// 세로
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if(r == i) continue;
if(sudoku[i][c] == sudoku[r][c]) return false;
}
return true;
}
}